1. Religious beliefs
- All of these were the polytheistic
- Babylonians professed by the peoples inhabiting the Tigris and Euphrates from what may be regarded as the dawn of history.
- Egyptian focused on afterlife, life after death and this led to the invention of mummification that was done to pharaohs.
- Phoenician religion was inspired by the powers and processes of nature.
2. Writing systems
- Phoenician writing system can be classified as an abjad, because it records only consonantal sounds, with the addition of matres lectionis for some vowels.
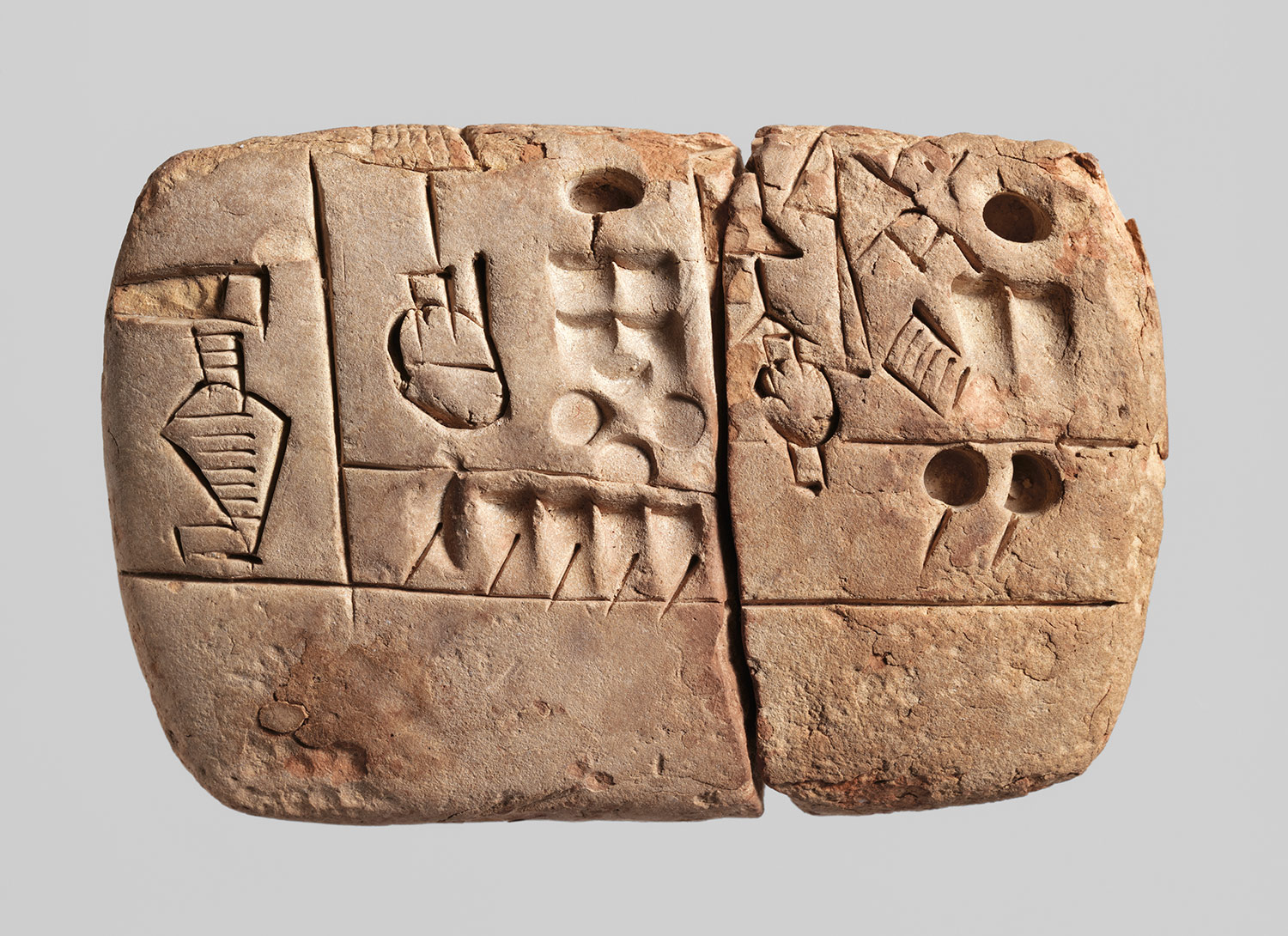
- Babylonian writing system called Cuneiform script and it began as a system of pictographs and written on clay tablets, by means of a blunt reed for a stylus.
- Egyptian writing system called Hieroglyphics that consisted of a series of pictures that represented letters and words.
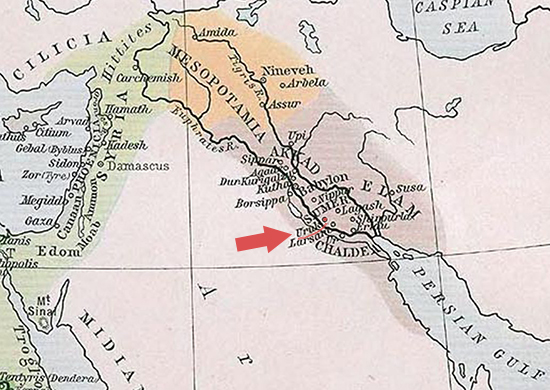
- All of them were located near the source of water.
- Phoenicians occupied a string of cities along the Mediterranean coast.
- Babylonian was located in Mesopotamia between the Tigris and the Euphrates River.
- Egyptians were located near the Nile River.
4. Agriculture advances
- The Phoenicians were not an agricultural people, because most of the land was not arable; therefore, they focused on commerce and trading instead.
- Agriculture formed the economic base of Babylonian civilization. People did a lot of farming from the river.
- Egyptians were very successful in agriculture, because they were able to farm the fertile soil around the Nile and produce their own food and cloth.
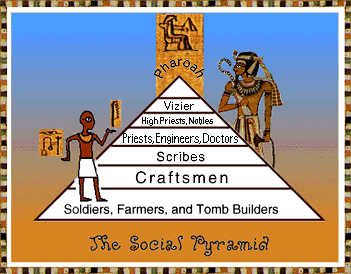
5. Social structure of Society
- Phoenicians where divided into three classes that citizens of Phoenicia were divided into. Social class was the top class which included priests, government officials, and land owners. The middle class included merchants, craftspeople, farmers, and fishermen. The working class included slaves and servants.
- For Babylonians, King was at the top, nobles (the free citizens) were at the middle and slaves were at the bottom.
- Ancient Egyptian’s social structure (right picture).
6. Technology advencement and inventions
- The Phoenicians first invented alphabet and they also built ships and the vessels that came to be known as the ships of Tarshish.
- Babylonian technology and invention: The zodiac; and eclipses of the sun and moon could be foretold, Mathematics, metalworking, copper-working, glassmaking, lamp making, textile weaving, flood control, and water storage, as well as irrigation.
- Egyptian technology and invention: pyramid, mummification, shadoof, locks, paper, plows, medicine, and eye make-up.
7. Trade routes
 - Phoenician trade routes in the Mediterranean. They also sailed out through the Pillars of Hercules, the Strait of Gibraltar up the coast of Europe to Britain.
- Phoenician trade routes in the Mediterranean. They also sailed out through the Pillars of Hercules, the Strait of Gibraltar up the coast of Europe to Britain.- The main foundation for Babylon's economy was trade routes between the Persian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea, as well as agriculture fed by the rich Euphrates River.
- Egyptians exported goods from several neighboring countries and they traded overseas such as Nubians.